If you’ve ever wondered what would happen if you cut sugar out of your diet for a whole month, you’re not alone. The 30-day sugar-free challenge has taken over TikTok, YouTube, and wellness blogs alike—with people reporting everything from rapid weight loss to mental clarity and radiant skin. But what really happens inside your body when you quit sugar for 30 days?
In this article, we’ll break down the real physiological, mental, and metabolic changes that occur when you eliminate added sugars from your diet. From sugar withdrawal symptoms to long-term health gains, you’ll discover what to expect, why it matters, and how to make the transition stick. Whether you’re doing this for weight loss, energy, or just to kick cravings, understanding the science behind sugar detox can help you stay committed.
Week-by-Week Breakdown: What Happens Inside Your Body
One of the most fascinating aspects of quitting sugar is how rapidly your body begins to respond. Let’s explore what each week typically looks like during a 30-day sugar detox.
Week 1 – Withdrawal, Cravings, and Mood Swings
The first few days are often the hardest. Your brain has become accustomed to sugar hits that stimulate dopamine, the “feel-good” hormone. When you remove sugar, your body essentially goes through withdrawal.
Common symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Sugar cravings
- Sleep disturbances
Week 2 – Stabilizing Energy and Appetite
Around days 8–14, your insulin levels begin to regulate more efficiently. Without frequent blood sugar spikes and crashes, your energy levels stabilize. You may also notice you’re less “hangry” between meals.
Changes you might feel:
- Fewer energy crashes
- Improved appetite control
- Slight weight loss (primarily water weight)
Week 3 – Mental Clarity and Improved Digestion
By now, most sugar withdrawal symptoms have faded. Many people report improved focus, less brain fog, and smoother digestion. This is largely due to reduced inflammation and a more balanced gut microbiome.
Improvements often reported:
- Better focus and memory
- Clearer skin
- Less bloating
Week 4 – Sustained Energy and Long-Term Gains
By the final stretch, your body has adapted to burning fat more efficiently. Inflammatory markers are reduced, and your metabolic health begins to reflect the benefits.
Long-term gains include:
- Lower blood pressure
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Continued fat loss
- Better sleep quality
How Sugar Affects Your Brain and Hormones
Quitting sugar doesn’t just influence your waistline—it fundamentally shifts the way your brain and endocrine system operate. Understanding these shifts is crucial if you want long-term motivation to stay off added sugars.
Dopamine Disruption—Why Sugar Feels So Good
Every time you consume sugary foods, your brain releases a surge of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that controls the pleasure and reward centers. This is why sugary treats often feel comforting or even addictive.
According to studies published in the journal Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews and supported by NIH research, sugar consumption stimulates the brain in ways similar to drugs like cocaine and morphine. Over time, this leads to tolerance—where you need more sugar to feel the same pleasure—and withdrawal, which explains why quitting feels so difficult at first.
Key points:
- Sugar hijacks your reward system
- Repeated spikes dull dopamine receptors
- This leads to sugar dependence and emotional eating
The Insulin Effect—Metabolic Chaos from Too Much Sugar
Insulin is a hormone that helps transport glucose from your blood into cells for energy. When you consume large amounts of sugar regularly, your body starts producing more insulin. Over time, this leads to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
When you quit sugar:
- Insulin levels decrease
- Cells regain insulin sensitivity
- Risk of type 2 diabetes is reduced
A study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation revealed that just two weeks on a high-sugar diet led to elevated insulin and fat storage in healthy adults. Cutting out added sugars, even short-term, helps reverse this trend.
Cortisol and Sleep—Sugar’s Hidden Stress Link
Few realize that sugar impacts cortisol, the stress hormone. Excessive sugar intake causes blood sugar fluctuations, which your body interprets as stress. As a result, cortisol is released, creating a vicious cycle of stress-eating and poor sleep.
When you quit sugar:
- Cortisol levels stabilize
- Sleep cycles improve
- Morning energy is higher
Ghrelin and Leptin—Resetting Hunger and Satiety Signals
Ghrelin and leptin are two hormones that regulate hunger and fullness. Sugar disrupts both:
- Ghrelin (hunger hormone): Increases when blood sugar drops quickly after a sugar spike.
- Leptin (satiety hormone): Becomes less effective over time with high sugar diets.
After 30 days sugar-free:
- Ghrelin levels normalize
- Leptin sensitivity improves
- You feel satisfied with less food
Physical Benefits of a 30-Day Sugar Detox
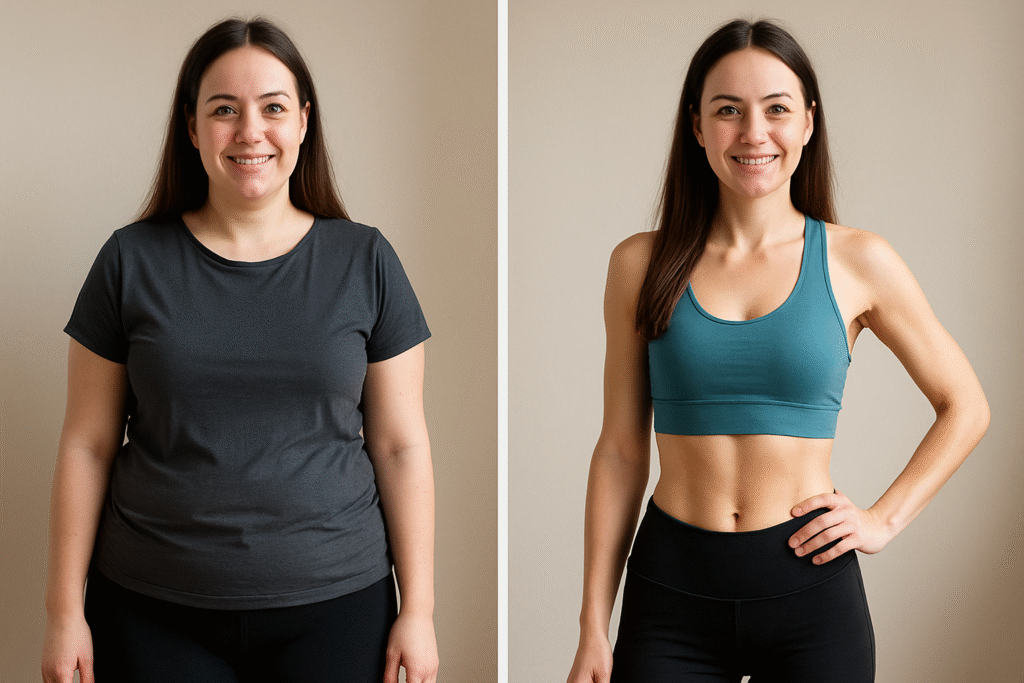
Quitting sugar isn’t just a theoretical health hack—it manifests in tangible, visible ways. From your skin to your gut, nearly every organ system benefits when you eliminate added sugars. Here’s a closer look at the most impactful physical transformations your body undergoes in just 30 days.
Weight Loss—Less Sugar, Fewer Calories, More Fat Burn
The most noticeable result of a sugar detox is usually weight loss. Sugar is calorie-dense and nutrient-poor, and it often triggers overeating due to its addictive nature. When you remove it:
- Your daily caloric intake drops naturally
- Your appetite-regulating hormones (ghrelin/leptin) rebalance
- Your body shifts from glucose to fat as its primary energy source
Studies show that eliminating sugary beverages alone can reduce total daily calorie intake by over 300 kcal. Over 30 days, this can translate into 2–4 pounds of fat loss, depending on other dietary habits.
✅ Expert SummaryClearer Skin—Reduced Acne and Inflammation
Sugar is a known pro-inflammatory agent. As Healthline explains, it spikes insulin, which can increase sebum production and androgen activity—two major contributors to acne.
When you quit sugar:
- Inflammatory markers decline
- Hormonal balance improves
- Skin becomes clearer, less oily, and more even-toned
Digestive Harmony—Less Bloating, Better Gut Health
Added sugars—especially in processed foods—feed harmful gut bacteria like Candida albicans. This can cause digestive issues like bloating, gas, and irregular bowel movements.
Benefits of quitting sugar for gut health:
- Reduced dysbiosis (microbial imbalance)
- Less gas and bloating
- Improved nutrient absorption
A 2022 NIH study found that people on sugar-free diets had higher levels of short-chain fatty acids—important for colon health and immune regulation.
Immune System Reinforcement
Excess sugar consumption is linked to suppressed immune response. High glucose levels impair the function of neutrophils (white blood cells), making you more vulnerable to infections.
Benefits after 30 days without sugar:
- Increased white blood cell activity
- Reduced systemic inflammation
- Better resilience against colds and flu
| Body System | Positive Change |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | Improved fat burning, reduced insulin resistance |
| Skin | Less acne, reduced oiliness, improved tone |
| Gut | Better digestion, less bloating, enhanced microbiome |
| Immune System | Stronger response, lower inflammation markers |
| Weight | Fat loss, fewer cravings, stabilized appetite |
What the Research Says
The benefits of quitting sugar aren’t just anecdotal—they’re firmly rooted in decades of peer-reviewed research. From metabolic health to mental clarity, the scientific community has amassed compelling evidence that eliminating added sugars leads to measurable improvements in key health markers.
Sugar and Metabolic Health—Clinical Evidence of Risk and Reversal
One of the most cited studies in this area comes from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). Researchers led by Dr. Robert Lustig conducted a controlled trial with children who were put on a low-sugar diet for 9 days. Remarkably:
- Fasting blood glucose levels dropped by 53%
- LDL cholesterol levels decreased by 10%
- Blood pressure improved significantly
This study, published in Obesity, demonstrates that even without reducing total calorie intake, removing sugar improved metabolic markers rapidly.
Another study published in JAMA Internal Medicine in 2014 linked high-sugar diets to a 38% increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, regardless of physical activity or body weight. These findings underscore that sugar’s impact extends far beyond calorie count—it’s a metabolic disruptor.
Cognitive and Emotional Benefits—Less Sugar, Better Brain
In 2020, a meta-analysis published in Nutritional Neuroscience found that high sugar intake is associated with higher rates of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline in adults. The mechanism? Chronic sugar consumption increases oxidative stress and systemic inflammation, both of which impair brain function.
Quitting sugar leads to:
- Reduced brain inflammation
- Enhanced neuroplasticity
- Lower risk of mood disorders
Immune Response and Inflammation—The Anti-Sugar Effect
A pivotal 1973 study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition revealed that consuming 100 grams of sugar significantly reduced white blood cell activity for up to five hours. More recent studies have reinforced these findings.
In 2021, researchers from the University of Groningen found that high-sugar diets impair neutrophil and macrophage function, delaying immune response and increasing susceptibility to infection.
After quitting sugar:
- C-reactive protein (CRP) levels decrease
- Inflammatory cytokines reduce
- White blood cells function more efficiently
Gut Health—Feeding the Right Microbes
The human gut microbiome thrives on fiber-rich, low-sugar diets. High sugar intake promotes the growth of harmful bacteria like Candida albicans and Clostridium difficile, leading to dysbiosis.
A 2023 randomized controlled trial published in Gut Microbes found that participants who eliminated added sugars for 30 days experienced:
- Increased microbial diversity
- Higher levels of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium
- Reduced markers of gut inflammation
Psychological and Lifestyle Changes After Quitting Sugar

The benefits of quitting sugar go far beyond the physiological. As your brain chemistry stabilizes and your hormones rebalance, you’ll likely experience a profound shift in mindset, emotional regulation, and daily behavior. These changes can be just as transformative—and longer-lasting—as the physical improvements.
Improved Self-Control and Reduced Cravings
Sugar addiction operates on the same neural pathways as substance use. When you break the sugar cycle, your brain starts to regain executive function, allowing better decision-making and impulse control.
Over time:
- Cravings diminish
- Emotional eating becomes less frequent
- Mindful eating habits replace autopilot snacking
A study published in Appetite journal found that participants on a sugar-free diet reported greater perceived control over eating behaviors, especially in stressful or emotional scenarios.
Enhanced Mood Stability and Less Anxiety
As blood sugar stabilizes, so does your mood. Sugar-induced highs and crashes are often mistaken for “mood swings” or anxiety episodes. Removing added sugars helps level your emotional state, making you feel more grounded and balanced throughout the day.
Reported changes include:
- Fewer emotional outbursts
- Decreased feelings of panic or nervousness
- More patience and resilience in daily interactions
Better Focus, Memory, and Mental Clarity
One of the most celebrated benefits of quitting sugar is the sudden lift in “brain fog.” Within weeks, many individuals report:
- Sharper memory
- Quicker processing speed
- Enhanced concentration during tasks
This improvement stems from reduced inflammation, more stable glucose supply to the brain, and increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)—a key protein involved in learning and memory.
📌 Did You Know?Motivation and Productivity Boost
Mental clarity feeds directly into better productivity. Without the energy dips and mood crashes triggered by sugar, your day becomes more stable and focused. Many who quit sugar report:
- More consistent energy throughout the workday
- Improved motivation for physical activity
- Less procrastination
Conclusion
Quitting sugar for 30 days may seem like a daunting challenge, but the benefits—both physical and psychological—are undeniable. From weight loss and clearer skin to stabilized mood and heightened mental clarity, the transformation touches nearly every aspect of your health. More importantly, it sets the stage for long-term wellness, allowing your body and brain to function as they were designed to: without dependency, inflammation, or imbalance.
By understanding how sugar affects your systems and experiencing firsthand what happens when you eliminate it, you gain a deeper awareness of your body’s needs. This journey isn’t just about what you’re cutting out—it’s about what you’re making room for: real vitality, consistent energy, and empowered living.
📌 Main Takeaways
- Your brain reacts to sugar like an addictive substance, making withdrawal challenging but transformative.
- Hormones like insulin, cortisol, ghrelin, and leptin rebalance after quitting sugar, improving metabolism and appetite control.
- Visible benefits include weight loss, clearer skin, better digestion, and stronger immunity.
- Mental clarity, emotional stability, and productivity improve significantly within 30 days sugar-free.
- Scientific studies confirm the rapid improvements in metabolic and cognitive health when sugar is removed.
🔗 Further Reading in HTML
Explore More Genius Nutra Insights
Ready to take the next step in your wellness journey?
How to Eat Carbs Without Gaining Fat
Learn how to reintroduce healthy carbs post-sugar detox without sabotaging your results.
How to Boost Your Metabolism Naturally
Discover science-backed strategies to elevate your fat-burning potential and maintain long-term energy.
Advanced Mitochondrial Formula Review
Support your cellular energy systems as you transition into a sugar-free lifestyle.



