A high-protein meal plan for weight loss can help you shed fat without sacrificing muscle. Struggling to find that balance? You’re not alone. Many people cut calories only to find themselves weaker, hungrier, and stuck in a frustrating cycle of weight regain. The truth is, when it comes to sustainable fat loss and body composition, protein is king. It fuels your metabolism, curbs cravings, and most importantly—preserves your lean muscle mass.
This 7-day high-protein meal plan is designed specifically for those who want to lose fat while maintaining muscle. Whether you’re cutting for a physique goal, trying to reset your diet, or simply want to feel stronger and more energized, this plan offers the perfect balance of macro-friendly meals, nutrient density, and delicious variety. Let’s dive into what makes protein such a powerful ally—and how to structure your week for real results.
How a High-Protein Meal Plan for Weight Loss Preserves Muscle and Burns Fat
High-protein diets aren’t just a fitness trend—they’re backed by decades of science showing their effectiveness in fat loss, metabolic health, and preserving lean mass during caloric deficits. Understanding the physiological and metabolic advantages of protein can help you approach your 7-day plan with purpose and confidence.
The Thermic Effect of Protein
One of the hidden benefits of protein is its thermic effect—your body burns more calories digesting and metabolizing protein than it does carbs or fats. In fact, up to 30% of the calories from protein are used just to digest it. That means if you eat 100 calories of chicken breast, you might only absorb 70!
This creates a natural calorie-burning advantage that supports fat loss without requiring drastic restriction.
Muscle Retention and Protein Synthesis
When you lose weight, you’re not just losing fat—you risk losing muscle mass, especially if protein intake is low. Muscle isn’t just for bodybuilders; it supports metabolic rate, joint health, and long-term weight stability.
Protein stimulates muscle protein synthesis (MPS), the process of rebuilding and maintaining muscle. Studies show that diets providing 1.6–2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day are ideal for preserving lean mass during a cut.
Satiety and Appetite Control
Protein is the most satiating macronutrient. It helps regulate hunger hormones like ghrelin and peptide YY, which means fewer cravings and better adherence to your plan.
✅ Expert Summary
High-protein diets not only support fat loss but also reduce hunger and preserve muscle. The combination of thermogenesis, muscle protein synthesis, and hormonal regulation makes protein a triple-threat nutrient in any weight loss plan.
📌 Did You Know?
Eating 30g of protein per meal may optimize muscle synthesis—more effective than spreading small amounts across the day.
7-Day Meal Structure: Calories, Macros, and Portions Explained

Before diving into daily menus, it’s essential to understand how this 7-day high-protein plan is strategically built. It’s not just about adding chicken to your plate—it’s about designing every meal with a precise balance of macronutrients to optimize fat loss while preserving muscle mass.
Setting Your Calorie Target for Fat Loss
The first step is calculating your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)—the number of calories you burn in a day. Subtracting 15–20% from this number creates a sustainable calorie deficit.
Example:
- Female, 150 lbs, moderately active → TDEE ≈ 2,000 kcal
- Weight loss target = 1,600–1,700 kcal/day
- Male, 190 lbs, active → TDEE ≈ 2,500–2,700 kcal
- Weight loss target = 2,100–2,300 kcal/day
💡 Quick Tip
Use an online TDEE calculator or wearable fitness tracker for a more accurate baseline. Adjust weekly based on progress.
Protein Targets for Muscle Retention
Research supports consuming 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight for those in a calorie deficit aiming to preserve muscle.
- 150 lb woman → 105–135g protein/day
- 190 lb man → 133–190g protein/day
This intake is split across 4–5 meals daily to maintain steady muscle protein synthesis and satiety.
✅ Expert Summary
Eating 30–40g of high-quality protein in each major meal helps maximize muscle retention, energy levels, and metabolic function during fat loss.
Balancing Fats and Carbs Around Protein
While protein is the star, balanced fats and carbs are crucial for hormone health, performance, and satisfaction:
- Carbs (30–40% of calories): Fuel workouts and replenish glycogen.
- Fats (20–30% of calories): Support hormones and cell function.
Use these ranges as a guide:
| Nutrient | % of Daily Intake | Grams per Day (1,800 kcal example) |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 35–40% | 150–180g |
| Carbs | 30–40% | 135–180g |
| Fats | 20–30% | 40–60g |
How to Space Your Meals for Maximum Effect
Meal timing affects muscle retention, recovery, and hunger. A common structure:
- Breakfast: 30–40g protein + carbs
- Lunch: 30–40g protein + carbs + veg
- Post-Workout Snack: 25–30g protein + carb-rich fruit
- Dinner: 30–40g protein + fibrous veg + moderate fat
- Optional Casein Snack: 20g slow-digesting protein before bed
Macronutrient Breakdown by Goal Weight
| Goal Weight (lbs) | Calories | Protein (g) | Carbs (g) | Fats (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 130 | 1,500 | 110–130 | 120–140 | 40–50 |
| 160 | 1,800 | 130–150 | 135–165 | 50–60 |
| 190 | 2,100 | 150–180 | 150–180 | 60–70 |
The 7-Day High-Protein Meal Plan (Full Menu with Variations)
This comprehensive 7-day plan is crafted to deliver an average of 130–180 grams of protein per day, depending on individual needs. Each meal is built with clean proteins, fiber-rich veggies, healthy fats, and smart carbs to maximize satiety, energy, and lean muscle retention.
Day 1: Kickstart with Clean Energy
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt parfait with berries, chia seeds, and whey isolate (35g protein)
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast with quinoa and steamed broccoli (45g protein)
- Snack: Cottage cheese with cucumber slices and almonds (25g protein)
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted Brussels sprouts and sweet potato (40g protein)
- Optional: Casein protein shake before bed (25g)
Day 2: Fiber + Fuel
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs (3 whole, 3 whites) with spinach and Ezekiel toast (30g protein)
- Lunch: Turkey lettuce wraps with avocado and hummus, served with carrot sticks (40g protein)
- Snack: Protein smoothie with banana, oat milk, and vegan protein (30g protein)
- Dinner: Grass-fed beef stir-fry with mixed vegetables and jasmine rice (45g protein)
Day 3: Classic and Satisfying
- Breakfast: Protein pancakes with almond butter and strawberries (35g protein)
- Lunch: Tuna salad with chickpeas, olive oil, arugula, and red onion (40g protein)
- Snack: Hard-boiled eggs (2), beef jerky, and an apple (25g protein)
- Dinner: Lemon herb chicken thighs, farro, and asparagus (40g protein)
Day 4: Midweek Reset with Lean Proteins
- Breakfast: Protein oatmeal with flaxseeds and blueberries (30g protein)
- Lunch: Grilled tofu or tempeh bowl with lentils, kale, and tahini dressing (35g protein)
- Snack: Cottage cheese and a handful of walnuts (20g protein)
- Dinner: Cod fillet with mashed cauliflower and sautéed spinach (45g protein)
- Optional: Greek yogurt with cinnamon (20g)
Day 5: High-Energy Friday
- Breakfast: Egg white omelet with smoked salmon, spinach, and avocado (35g protein)
- Lunch: Chicken burrito bowl (grilled chicken, brown rice, black beans, salsa) (45g protein)
- Snack: Protein bar (clean-label, whey or plant-based) (20g protein)
- Dinner: Sirloin steak, roasted carrots, and green beans (45g protein)
Day 6: Weekend Strength Boost
- Breakfast: High-protein chia pudding with peanut butter and banana (30g protein)
- Lunch: Shrimp salad with olive oil, mixed greens, and wild rice (40g protein)
- Snack: Smoothie bowl with protein powder, berries, oats, and pumpkin seeds (30g protein)
- Dinner: Turkey meatballs with zucchini noodles and marinara (45g protein)
Day 7: Recovery + Hydration Focus
- Breakfast: Protein smoothie with collagen peptides, coconut milk, and spinach (35g protein)
- Lunch: Bison burger lettuce wrap with sweet potato fries (40g protein)
- Snack: Edamame with lemon and a boiled egg (20g protein)
- Dinner: Grilled mahi-mahi with wild rice and grilled zucchini (45g protein)
- Optional: Protein mousse (casein + Greek yogurt + cacao) (25g)
📌 Did You Know?
Mixing plant and animal proteins throughout the week diversifies amino acid intake and supports gut health and muscle synthesis.
Meal Prep Strategies and Shopping List Tips
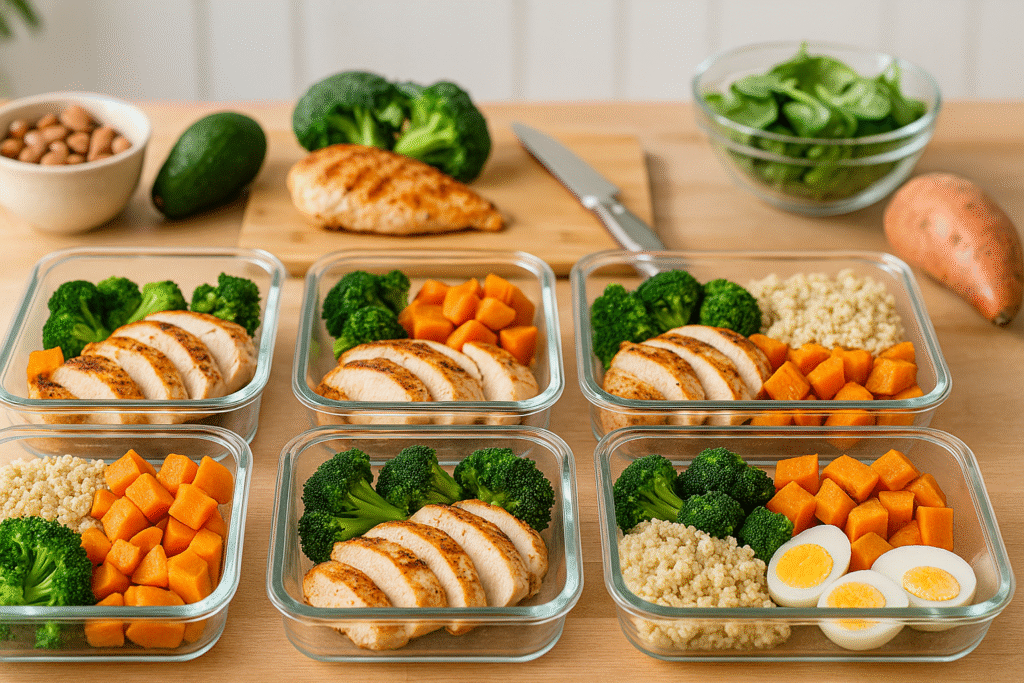
Planning is the secret weapon of successful weight loss. Without it, even the most well-designed meal plan can fall apart under the stress of a busy week. The good news? With just 2 to 3 hours per week, you can prepare all your protein staples, portion your meals, and stay on track.
Batch Cooking Basics
The goal is to minimize daily cooking by preparing large quantities of versatile ingredients. Here’s how to simplify the process:
- Choose 2–3 proteins per prep (e.g., chicken breast, salmon, tofu)
- Cook grains in bulk (quinoa, brown rice, oats)
- Chop and store veggies in clear containers for easy access
- Portion meals into containers with clear macros labeled
💡 Quick Tip
Use a food scale and labeling system to track protein content per container. Example: “Grilled chicken – 6 oz = 42g protein”.
Smart High-Protein Grocery List
Group your items by section to save time and reduce food waste:
Proteins
- Chicken breast, turkey breast, lean ground beef
- Eggs and egg whites
- Greek yogurt (plain, high-protein)
- Cottage cheese
- Whey/casein/vegan protein powder
- Tofu, tempeh, edamame
- Canned tuna and salmon
- Shrimp, cod, mahi-mahi
- Bison, grass-fed beef
Carbohydrates
- Quinoa, brown rice, sweet potatoes, oats
- Beans (black beans, chickpeas, lentils)
- Whole grain tortillas, sprouted grain bread
Fats
- Avocados, olive oil, nuts and seeds, almond butter
Vegetables
- Spinach, kale, arugula, broccoli, asparagus
- Carrots, bell peppers, onions, Brussels sprouts
Fruits
- Berries, bananas, apples, oranges
✅ Expert Summary
Prepping meals in advance improves consistency, reduces decision fatigue, and ensures your high-protein targets are met with ease—even on your busiest days.
Storage and Reheating Tips
- Use glass containers with divided sections for proteins, carbs, and veggies
- Label meals with date and macros
- Freeze meals that won’t be consumed within 4 days
- Reheat proteins gently to preserve texture (avoid microwave overheating)
What the Research Says: Protein and Fat Loss Efficiency
If you’re wondering whether high-protein diets are truly effective—or just another fitness fad—the answer is clear: science supports their role in weight loss, muscle retention, and metabolic health. Here’s what recent studies reveal about why protein matters so much.
Preserving Lean Mass During Caloric Deficit
A well-known clinical trial published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that diets higher in protein (up to 2.4g/kg/day) helped athletes retain significantly more lean mass during weight loss compared to those on moderate-protein diets【PubMed Study】.
Another study found that participants consuming 1.6g/kg of protein lost more fat and preserved more muscle than those consuming 0.8g/kg, even when calorie intake was identical【NIH source】.
Protein Improves Appetite and Satiety Hormones
Protein-rich meals enhance levels of appetite-regulating hormones like GLP-1 and PYY, while reducing ghrelin (the hunger hormone). A 2014 study confirmed that protein intake around 30% of total calories increased satiety and spontaneous calorie reduction【Healthline review】.
Metabolic Boost and Fat Oxidation
Protein increases the thermic effect of food (TEF), which boosts energy expenditure. In comparative studies, high-protein diets consistently showed elevated metabolic rates during fat loss phases compared to high-carb diets【PubMed Review】.
📌 Did You Know?
Eating 30% of your calories from protein may help burn up to 100 extra calories per day through digestion alone.
Conclusion
A successful weight loss plan doesn’t mean sacrificing strength or energy—it means being strategic. With this 7-day high-protein meal plan, you’re fueling your body to burn fat, retain lean muscle, and feel consistently satisfied. From smart portioning to science-backed protein intake, each day is a step toward sustainable results.
Remember: consistency beats perfection. Even small adjustments in protein intake, meal prep, and nutrient balance can yield impressive outcomes. Trust the process, fuel with intention, and watch your body respond with strength and resilience.
Main Takeaways
- High-protein diets boost metabolism and help preserve lean muscle during weight loss.
- Aim for 0.7–1 gram of protein per pound of body weight daily for muscle retention.
- Structure meals around 30–40g of protein for optimal results and satiety.
- Batch cooking and smart shopping save time and keep your diet on track.
- Scientific evidence confirms the fat-loss advantages of high-protein nutrition.
🔗 Further Reading
Think carbs ruin fat loss?
Learn how to eat carbs strategically without storing fat. How to Eat Carbs Without Gaining Fat
Looking for a natural fat-loss booster?
See how this plant-based superfood is changing the game. Moringa Magic Review




Pingback: Healthy Meal Prep: The Unexpected Strategy That Saved One Family’s Routine