Intermittent fasting has surged in popularity among health enthusiasts, weight loss seekers, and even longevity researchers. This eating pattern, which alternates between periods of eating and fasting, promises benefits like fat loss, improved metabolism, and enhanced mental clarity. But is it all positive? Like any health trend, intermittent fasting comes with both benefits and risks—some of which might surprise you.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore the real science behind intermittent fasting. We’ll dissect the benefits, highlight potential risks, compare fasting methods, and provide actionable advice for safely integrating it into your lifestyle. Whether you’re fasting-curious or a seasoned practitioner, this article gives you the full picture.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
Definition and Core Principles
Intermittent fasting (IF) is not a diet in the traditional sense—it’s an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. Rather than focusing on what you eat, IF emphasizes when you eat. The goal is to give your body extended periods without food, allowing it to reset key metabolic functions and potentially tap into fat stores for energy.
Fasting periods can range from a few hours to a full day or more, depending on the method. During these fasting windows, only non-caloric beverages like water, black coffee, and herbal teas are typically allowed.
📌 Did You Know?
Fasting has been practiced for thousands of years in various cultures, often for spiritual or health reasons. Today, it’s gaining attention for its potential to support weight loss, improve metabolic health, and increase longevity.
Common Intermittent Fasting Methods
There are several popular ways to structure your intermittent fasting schedule, each with its own benefits and challenges:
- 16:8 Method: Fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window (e.g., 12 pm–8 pm). One of the most beginner-friendly and sustainable approaches.
- 5:2 Method: Eat normally five days a week and consume only 500–600 calories on two non-consecutive days.
- OMAD (One Meal a Day): A more extreme form where all daily calories are consumed in a single meal, typically within 1 hour.
💡 Quick Tip:
Start with a 12:12 schedule (12 hours fasting, 12 hours eating) and gradually extend your fasting window as your body adapts.
Infographic: Comparison Table of Fasting Methods
| Fasting Method | Fasting Window | Eating Window | Ideal For | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16:8 | 16 hours | 8 hours | Beginners | Low |
| 5:2 | 2 days/week (500–600 kcal) | Normal eating on other days | Weight loss | Moderate |
| OMAD | 23 hours | 1 hour | Advanced | High |
Proven Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Weight Loss and Metabolic Boost
One of the most popular reasons people try intermittent fasting is for weight loss. By shortening the eating window, many naturally reduce their calorie intake without strict dieting. Additionally, fasting triggers hormonal changes that boost metabolism:
- Insulin levels drop, encouraging fat burning.
- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) increases, aiding muscle gain and fat loss.
- Norepinephrine levels rise, enhancing energy and fat oxidation.
According to a 2020 review in The New England Journal of Medicine, intermittent fasting can lead to a 3–8% weight reduction over 3–24 weeks, especially when combined with whole-food nutrition.
💡 Quick Tip:
Drink water or black coffee during fasting windows to curb hunger and stay hydrated.
Brain Health and Mental Clarity
Fasting doesn’t just benefit the body—it may sharpen the mind as well. During fasting periods, the brain experiences:
- Increased production of BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), linked to cognitive function and learning.
- Enhanced neuroplasticity and stress resistance.
- Reduced inflammation, which contributes to mental fog and fatigue.
Animal studies have even shown that fasting may protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
📌 Did You Know?
Some people report heightened focus and mental clarity during fasting, especially after the first week of adaptation.
Longevity and Cellular Repair (Autophagy)
One of the most exciting discoveries about intermittent fasting is its role in autophagy—the process by which the body cleans out damaged cells and regenerates new ones.
This process:
- Reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
- Supports healthy aging.
- May extend lifespan (as observed in animal studies).
A 2016 Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded for research on autophagy, further validating its importance in disease prevention and cellular health.
✅ Expert Summary:
Fasting can do more than slim your waistline—it may rejuvenate your cells, boost brain function, and contribute to a longer, healthier life.
Scientific Studies on Fasting Results
| Study | Focus Area | Result Summary | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEJM 2020 | Metabolism & Weight | 3–8% body weight loss in 3–24 weeks | NEJM |
| Cell Metabolism 2014 | Brain Health | Increased BDNF, improved cognition in mice | Cell.com |
| Science 2016 | Autophagy | Validated cellular renewal through fasting | Science.org |
Hidden Risks and Common Side Effects
Nutritional Deficiencies and Muscle Loss
While intermittent fasting can support fat loss, it may inadvertently lead to nutritional gaps if meals during the eating window lack balance. People who rush meals or skip vegetables and proteins may miss essential nutrients like:
- Iron, calcium, magnesium
- Fiber and essential fatty acids
- Vitamin B12 and D
Another concern is muscle loss, especially in people who fast without maintaining protein intake or strength training. When calorie intake drops too low, the body may break down muscle tissue for energy.
📌 Did You Know?
Muscle loss during fasting can slow down your metabolism, making it harder to maintain weight loss over time.
Hormonal Imbalances and Women’s Health
Fasting affects hormones—and while that can be beneficial, it also poses risks, particularly for women:
- Disrupted menstrual cycles or amenorrhea
- Lowered thyroid function in some individuals
- Increased stress hormones like cortisol
Women of reproductive age or those with PCOS, thyroid disorders, or a history of disordered eating should approach fasting cautiously and consider modified versions like 12:12 or 14:10.
💡 Quick Tip:
If you’re a woman experiencing fatigue, mood swings, or irregular cycles while fasting, consult a health professional and consider shortening your fasting window.
Risk for People with Health Conditions
Fasting isn’t suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain health conditions should avoid or closely monitor intermittent fasting:
- Diabetics or those on insulin medication (risk of hypoglycemia)
- Underweight individuals or those recovering from eating disorders
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- People with gastrointestinal disorders (e.g., GERD, ulcers)
✅ Expert Summary:
While fasting offers many benefits, it must be done mindfully. Ignoring personal health conditions or failing to meet nutritional needs can backfire.
Case Analysis or Medical Expert Insight
“In my practice, I’ve seen great results with intermittent fasting—but only when it’s personalized. A one-size-fits-all approach can do more harm than good, especially for women or patients with thyroid or adrenal issues.”
— Dr. Laura Mendelson, Functional Nutritionist
How to Start Intermittent Fasting Safely

Step-by-Step Fasting Plan for Beginners
Starting intermittent fasting can feel overwhelming—but with the right approach, your body can adapt smoothly. Here’s a simple 4-step plan:
- Choose Your Method: Start with a manageable schedule like 12:12 or 14:10.
- Ease Into It: Gradually increase fasting duration over 1–2 weeks.
- Stay Consistent: Pick consistent eating windows that match your lifestyle (e.g., 10 am–6 pm).
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to hunger, energy levels, and mood.
📌 Did You Know?
Most people naturally fast 8–10 hours overnight. Extending that by just 2–4 hours can activate metabolic benefits without major disruption.
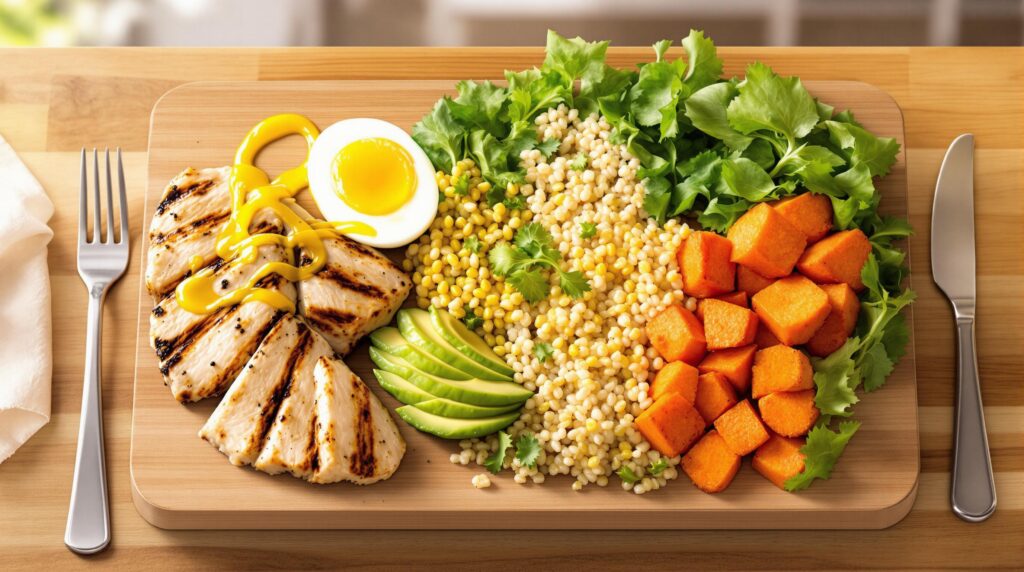
Foods to Eat and Avoid During Eating Windows
To maximize fasting benefits, focus on nutrient-dense meals that support satiety and metabolic health:
✅ Best Foods:
- Lean proteins (chicken, turkey, eggs, tofu)
- Healthy fats (avocados, nuts, olive oil)
- Complex carbs (quinoa, sweet potatoes, legumes)
- High-fiber veggies (broccoli, spinach, carrots)
❌ Foods to Avoid:
- Sugary snacks, baked goods, sodas
- Processed meats and trans fats
- Refined carbs (white bread, pasta)
- Excess caffeine on an empty stomach
💡 Quick Tip:
Break your fast with a balanced meal—avoid overloading on carbs or sugar right after a long fast.
Tracking Tools and Hydration Tips
Staying hydrated and tracking your progress are key to sustainable results:
Hydration Essentials:
- Drink water regularly throughout the fast.
- Add electrolytes or a pinch of Himalayan salt if fasting over 16 hours.
- Herbal teas and black coffee are allowed (no cream or sugar).
Tracking Tools:
- Apps like Zero, FastHabit, and MyFitnessPal
- Journals for mood, hunger levels, and energy
- Smartwatches with fasting timers and reminders
✅ Expert Summary:
Successful fasting is about more than just not eating—it’s about how you eat, hydrate, and track your body’s signals for long-term health.
Visual Meal Schedule Example
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| 7:00 am | Drink water + light movement (no food) |
| 10:00 am | Black coffee or herbal tea |
| 12:00 pm | Break fast with protein + fiber meal |
| 3:00 pm | Light snack (fruit + nuts) |
| 6:00 pm | Dinner: lean protein + veggies |
| 8:00 pm | Fasting begins, water only |
Advanced Tips and Optimization Strategies
Adjusting Fasting for Fitness and Workouts
One of the biggest questions about intermittent fasting is: Can I still work out while fasting? The answer is yes—with strategic adjustments:
- Fast Before Cardio: Light to moderate cardio (e.g., walking, cycling) can be done safely in a fasted state, promoting fat burn.
- Strength Training: If lifting weights, try to train near the end of your fast and eat protein soon after to support muscle repair.
- Post-Workout Fuel: Prioritize a mix of protein + complex carbs within 30–60 minutes of exercising.
📌 Did You Know?
Fasted training can enhance fat oxidation, but performance may suffer if glycogen stores are depleted—test what works best for your body.
Supplement Support While Fasting
Some supplements can enhance fasting benefits or support nutrient balance, even during extended fasts. Consider:
✅ Safe During Fasting (Zero Calories):
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium)
- Apple cider vinegar (diluted, under 5ml)
- Black coffee or green tea (antioxidant-rich)
- Adaptogens (like ashwagandha, if in capsule form)
❌ Breaks Fast:
- Protein powders, BCAAs
- Gummy vitamins or anything with sugar
- Anything with added calories or artificial sweeteners
💡 Quick Tip:
Always read labels—many “healthy” supplements contain hidden sweeteners or fillers that break your fast.
Lifestyle Integration and Long-Term Success
To make fasting a sustainable lifestyle:
- Be Flexible: Allow for social events and occasional changes without guilt.
- Cycle It: Practice fasting in intervals—like 5 days on, 2 days off—to prevent metabolic slowdown.
- Combine with Whole-Food Nutrition: IF is more effective when paired with an anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense diet.
✅ Expert Summary:
The key to successful intermittent fasting isn’t perfection—it’s personalization. Tailor your method, diet, and exercise to your unique biology and goals.
Fasting Success Checklist (Printable or Downloadable)
| ✔ | Habit |
|---|---|
| ☐ | I chose a realistic fasting window for my lifestyle |
| ☐ | I stay hydrated throughout the day |
| ☐ | I break my fast with protein-rich meals |
| ☐ | I adjust fasting on workout days |
| ☐ | I track my energy, sleep, and progress weekly |
| ☐ | I remain flexible and consistent, not obsessive |
How to Apply This to Your Routine
Daily and Weekly Fasting Routine
Consistency is the backbone of intermittent fasting. Here’s how to build a sustainable weekly plan:
Sample Weekly Routine (16:8 Method)
| Day | Eating Window | Fasting Window | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | 12 pm – 8 pm | 8 pm – 12 pm | Start week light, stay hydrated |
| Tuesday | 1 pm – 9 pm | 9 pm – 1 pm | Push back eating to test hunger |
| Wednesday | 12 pm – 8 pm | 8 pm – 12 pm | Add light morning workout |
| Thursday | 1 pm – 9 pm | 9 pm – 1 pm | Hydration + protein focus |
| Friday | 12 pm – 8 pm | 8 pm – 12 pm | Higher-carb day post workout |
| Saturday | Flexible | ~12 hours fast | Social meal flexibility |
| Sunday | Rest | No fasting | Full recovery & reflection |
📌 Did You Know?
Taking 1–2 “off” days a week may help you avoid stress and enhance adherence over time.
7-Day Beginner Challenge
Want to test intermittent fasting without a major lifestyle change? Try this 7-day introduction:
| Day | Goal |
|---|---|
| 1 | Fast 12 hours overnight |
| 2 | Try 13 hours (drink water) |
| 3 | Eat clean during meals |
| 4 | Fast 14 hours + light walk |
| 5 | Push to 15 hours (optional) |
| 6 | Repeat 14–15 hours + journal |
| 7 | Reflect on progress |
💡 Quick Tip:
Use a fasting app to track your streak—it boosts motivation and shows real-time progress.
Smart Habit Tracker and Reminders
Build your fasting routine with small but powerful tools:
- Reminders: Set alarms for meal start and end times.
- Journaling: Log mood, cravings, energy, and sleep.
- Habit stacking: Pair fasting with other healthy routines like stretching, meditation, or cold showers.
✅ Expert Summary:
Sustainable fasting starts with structure. Use a schedule, test what works, and stay consistent without being rigid.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting is more than a trend—it’s a powerful tool for those seeking a healthier, leaner, and more focused life. From metabolic improvements and fat loss to brain function and cellular renewal, its benefits are well supported by science. However, it’s essential to approach fasting with care, especially if you have underlying health conditions or specific nutritional needs.
By understanding the risks, choosing the right fasting window, and tailoring your approach with the strategies shared in this article, you can turn intermittent fasting into a sustainable and rewarding lifestyle shift.
Whether you’re just starting or refining your routine, intermittent fasting offers a natural, flexible way to enhance your wellness journey.
Main Takeaways
- Intermittent fasting focuses on when you eat—not what you eat.
- Benefits include fat loss, improved metabolism, brain function, and autophagy.
- Risks include nutrient deficiencies, muscle loss, and hormonal imbalances, especially for women.
- Start safely with a 12:12 or 16:8 method and monitor your body’s signals.
- Use tools like fasting apps, checklists, and hydration support to optimize results.
- Consistency and flexibility are key to long-term success.
Further Reading
Explore more in our Genius Nutra guides:



